Unlocking the Benefits: Wastezon 2.0 and Wastezon X
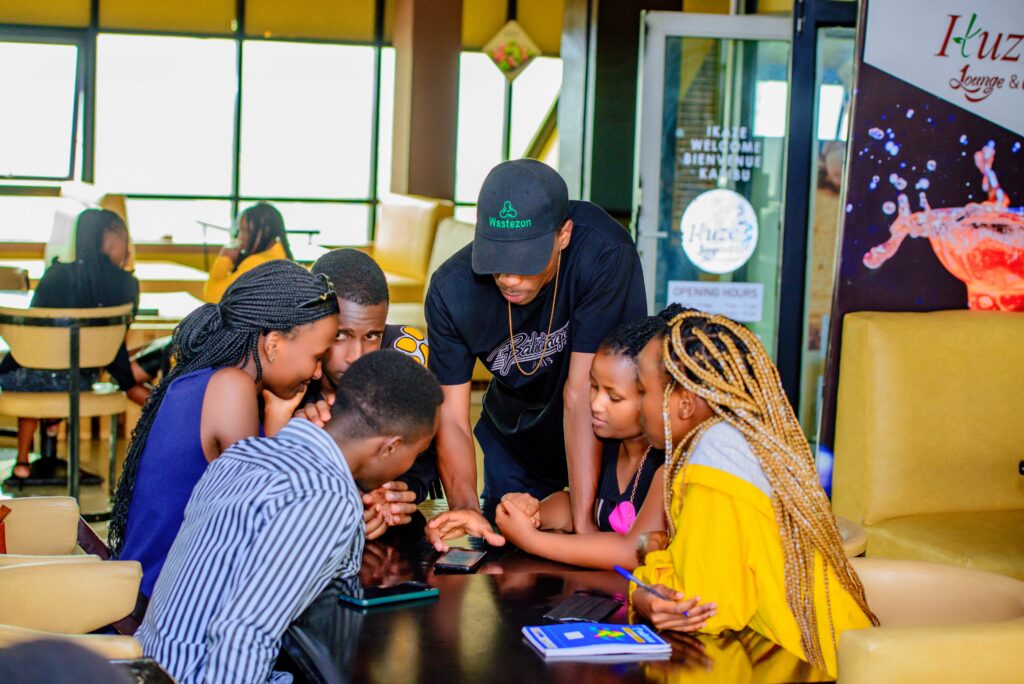


Introduction: As the digital landscape continues to evolve, Wastezon remains committed to driving innovation and delivering tangible benefits to its users. Wastezon 2.0 and Wastezon X exemplify the platform’s dedication to sustainability and customer satisfaction.
Wastezon 2.0 represents a significant upgrade from its predecessor, offering users an enhanced experience and a wealth of new features. From seamless device listings and intuitive search functionalities to secure payment options and streamlined recycling processes, Wastezon 2.0 sets a new standard for electronic waste management platforms.

Meanwhile, Wastezon X stands out as a game-changer in the realm of reverse supply chain management. By providing manufacturers, recyclers, and institutional consumers with unprecedented visibility and control over their operations, Wastezon X empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions and optimize resource utilization.
The benefits of Wastezon 2.0 and Wastezon X extend beyond convenience and efficiency. By promoting the reuse and recycling of electronic devices, Wastezon helps reduce the environmental impact of e-waste while fostering a culture of sustainability among its users.
Call to Action: Experience the benefits of Wastezon 2.0 and Wastezon X firsthand by signing up for an account today. Join us in our mission to build a more sustainable future through innovation, collaboration, and responsible consumption.
Introduction:
In today’s world, the concept of a circular economy has gained significant traction as a sustainable alternative to the traditional linear economic model. A circular economy aims to minimize waste and resource use by keeping products and materials in use for as long as possible, thereby maximizing their value. Wastezon, a pioneering platform in the realm of electronic waste management, is at the forefront of driving the circular economy forward.

Wastezon’s innovative approach revolves around redefining the future of urban mining through three core principles: resell, reuse, and remanufacture. By empowering users to resell their old electronic devices, facilitating the reuse of functional components, and remanufacturing products to extend their lifecycle, Wastezon is instrumental in reducing the environmental impact of e-waste.
Wastezon 2.0, the latest iteration of the platform, introduces a host of features designed to streamline the process of buying, selling, and recycling electronic devices. With an intuitive interface and enhanced functionalities, Wastezon 2.0 makes it easier than ever for users to participate in the circular economy.
Moreover, Wastezon X represents a significant leap forward in the journey towards sustainability. This integrated platform leverages cutting-edge technology, including machine learning algorithms, to optimize materials traceability and facilitate efficient transactions across the reverse supply chain.
Call to Action:
Join Wastezon in its mission to build a circular economy by downloading Wastezon 2.0 or exploring Wastezon X today. By embracing sustainable practices and contributing to the circular economy, we can collectively pave the way for a greener and more resilient future.
Urban Mining and the Role of Material Science in the Circular Economy
In the quest for sustainable resource management and reducing environmental impact, the concept of the circular economy has gained immense traction. At the heart of this paradigm shift lies the intriguing concept of urban mining, an innovative approach that redefines waste as a valuable resource. Coupled with the insights of material science, urban mining holds the promise of revolutionizing how we view, use, and recycle materials within a circular economy framework.
Understanding Urban Mining: Turning Waste into Resources
Urban mining is the process of recovering valuable resources from discarded electronic devices, appliances, and other products, often referred to as electronic waste (e-waste) or urban ore. Unlike traditional mining, which extracts raw materials from the Earth’s crust, urban mining involves extracting precious metals and other reusable components from discarded products. This approach not only conserves natural resources but also minimizes the environmental footprint associated with mining activities.
The Circular Economy Connection
The circular economy seeks to decouple economic growth from the consumption of finite resources. By promoting practices that prioritize reuse, recycling, and the extension of product life cycles, the circular economy aims to create a regenerative system where waste is minimized, and resources are continuously looped back into the production cycle. Urban mining aligns seamlessly with this vision, as it allows for the recovery of valuable materials from discarded products, reintroducing them into the production process and reducing the need for virgin resources.
Material Science’s Crucial Role
Material science plays a pivotal role in unlocking the potential of urban mining within the circular economy framework. Here’s how:
- Resource Identification: Material scientists are instrumental in identifying the composition of products and understanding the intricate blend of materials used in electronics and appliances. This knowledge is vital for efficient separation and recovery processes during urban mining.
- Innovative Extraction Techniques: Urban mining relies on advanced extraction techniques to recover valuable materials from complex electronic waste. Material scientists develop and refine these techniques to ensure high yields and minimal environmental impact.
- Material Characterization: Understanding the properties and behavior of recovered materials is essential for determining their potential applications. Material scientists analyze recovered materials to ascertain their suitability for reuse in various industries.
- Recyclability Design: Material scientists collaborate with designers and engineers to develop products with enhanced recyclability. By incorporating materials that are easier to separate and recycle, the lifespan of these materials can be extended, reducing waste.
- Quality Control: Ensuring the quality and reliability of recycled materials is crucial for their successful integration into new products. Material scientists play a role in developing standards and quality control processes for recycled materials.
The Path Forward: Collaboration and Innovation
For urban mining to reach its full potential, collaboration between various stakeholders is paramount. Governments, industries, academia, and consumers must work together to create efficient collection systems, establish recycling infrastructure, and promote awareness about the value of recycled materials.
As the world grapples with the challenges of resource scarcity and environmental degradation, urban mining, propelled by the insights of material science, emerges as a beacon of hope. By turning waste into resources and contributing to the circular economy, urban mining offers a tangible solution to the global sustainability puzzle. With continued research, innovation, and concerted efforts, this transformative approach has the power to reshape industries and pave the way toward a more sustainable and resilient future.
This blog post was authored by a member of our team to share their insights and expertise on the topic.
On this World Environment Day, we celebrate the coming together of two innovative entities committed to creating a sustainable future: Wastezon, a dynamic startup revolutionizing the circular economy, and Kigali Green Gallery, a youth-led NGO dedicated to biodiversity conservation through creative avenues. By harnessing the power of technology and art, these organizations are making significant strides in waste management and environmental education. Let’s explore their endeavours and how they are shaping a greener world.
World Environment Day, observed on June 5th every year, is a global initiative to raise awareness about environmental issues and encourage positive action. It serves as a reminder that we all have a responsibility to protect and preserve our planet for future generations. This year’s theme is #BeatPlasticPollution; its sub-focus, Circular economy resonates with Wastezon’s mission to create a waste-free world.
At the core of Wastezon’s mission is the commitment to provide consumers, manufacturers, and recyclers with efficient traceability services that generate waste-value addition benefits in an environmentally friendly way. By offering transparent solutions and promoting a circular economy, Wastezon aims to minimize waste, maximize resource efficiency, and create a more sustainable and responsible future.
Wastezon 2.0, a highly anticipated application revolutionized peer-to-peer transactions. By leveraging cutting-edge mineralogical laser scan technology, the app captures the provenance levels of products, ensuring price transparency and predicting durability. Household consumers gain access to secure and quality-vetted second-hand electronics, empowering them to make informed decisions regarding repairs and future returnability needs. Institutional consumers can make sustainable purchasing decisions by accessing products with certified provenance.

Their second upcoming product, WastezonX is a B2B web app platform that complements Wastezon 2.0 by providing traceability and tracking infrastructures for manufacturers and recyclers. It enables efficient materials returnability and reverse supply chain management. Manufacturers and recyclers can acquire products based on vetted materials provenance and leverage logistic planners to arrange reverse logistics, promoting a more sustainable and efficient materials management system.
By bridging sustainable practices and technological advancements, Wastezon’s products cater to diverse audiences, offering comprehensive solutions for consumers, manufacturers, and recyclers.
In line with the theme of World Environment Day, Kigali Green Gallery is a youth-led non-profit organization that amplifies the impact of biodiversity conservation education using creative avenues, particularly art. Their recent documentary, “Biodiversity Through the Ages,” engages the community by inviting elders to share their conservation thoughts with younger generations.
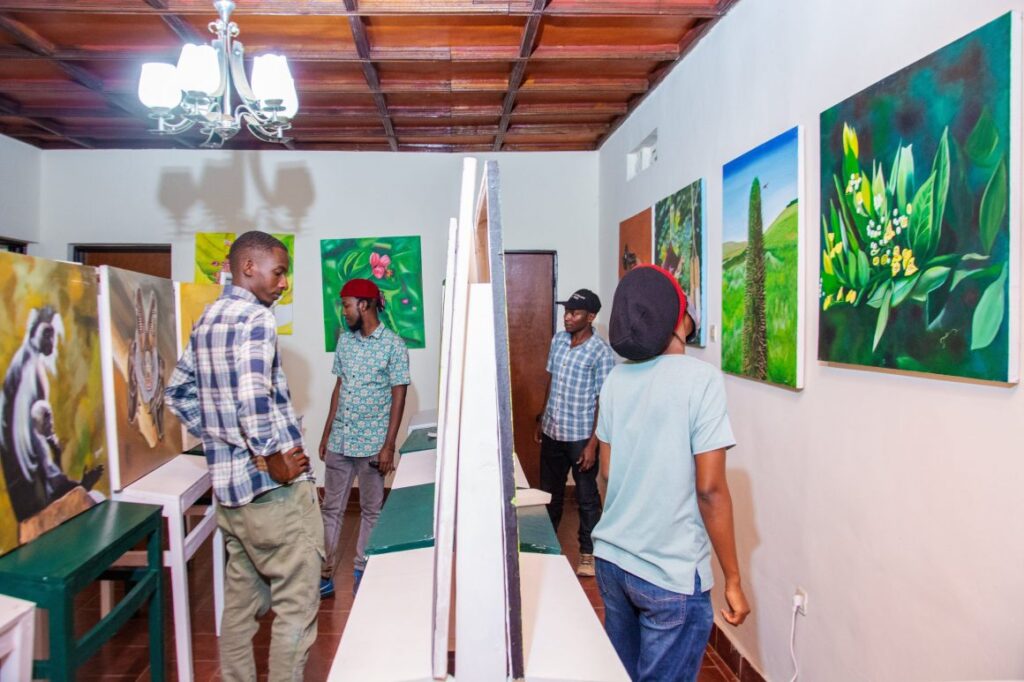

By blending storytelling, art, and community involvement, Kigali Green Gallery nurtures a deep connection with nature. They inspire individuals to appreciate and protect biodiversity, fostering a sense of responsibility for our environment. Through their initiatives, the organization seeks to build awareness, understanding, and action for the preservation of ecosystems.
The work shared between Wastezon and Kigali Green Gallery signify a joint effort to tackle environmental challenges comprehensively. Wastezon’s focus on circular economy and urban mining aligns perfectly with Kigali Green Gallery’s mission to promote biodiversity conservation through creative avenues.
By incorporating the principles of waste-value addition and sustainable materials management, Wastezon’s products contribute to reducing environmental impact. Moreover, Kigali Green Gallery’s artistic approach to biodiversity conservation education offers a unique platform for raising awareness and inspiring positive change.
Together, Wastezon and Kigali Green Gallery are working towards a common goal: fostering a waste-free world and preserving biodiversity. They provide solutions that empower individuals, manufacturers, and recyclers to make sustainable choices while engaging communities in conservation conversations.
As we commemorate World Environment Day, it is crucial to recognize and support organizations like Wastezon and Kigali Green Gallery, who are championing sustainability and biodiversity conservation through their innovative approaches. Wastezon’s products bridge the gap between sustainable practices and technological advancements, enabling consumers, manufacturers, and recyclers to contribute to a circular economy. Simultaneously, Kigali Green Gallery’s focus on creative avenues, particularly art, enhances biodiversity conservation education.
By embracing technology, art, and community involvement, Wastezon and Kigali Green Gallery exemplify the power of collaboration in creating a greener, more sustainable world. On this day, let us join hands with these organizations and make a collective commitment to preserve our environment and ensure a better future for generations to come.
Climate change has become a pressing issue that poses a significant threat to human health. The effects of climate change are far-reaching and can result in various health problems. The link between human health and climate change is complex, and it is essential to understand its impact on our well-being.
One of the most significant impacts of climate change on human health is the increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as hurricanes, floods, and heat waves. These events can lead to injuries, fatalities, and mental health issues such as anxiety and depression. The rising temperatures and heat waves can also exacerbate respiratory and cardiovascular diseases, especially in vulnerable populations such as the elderly and children.
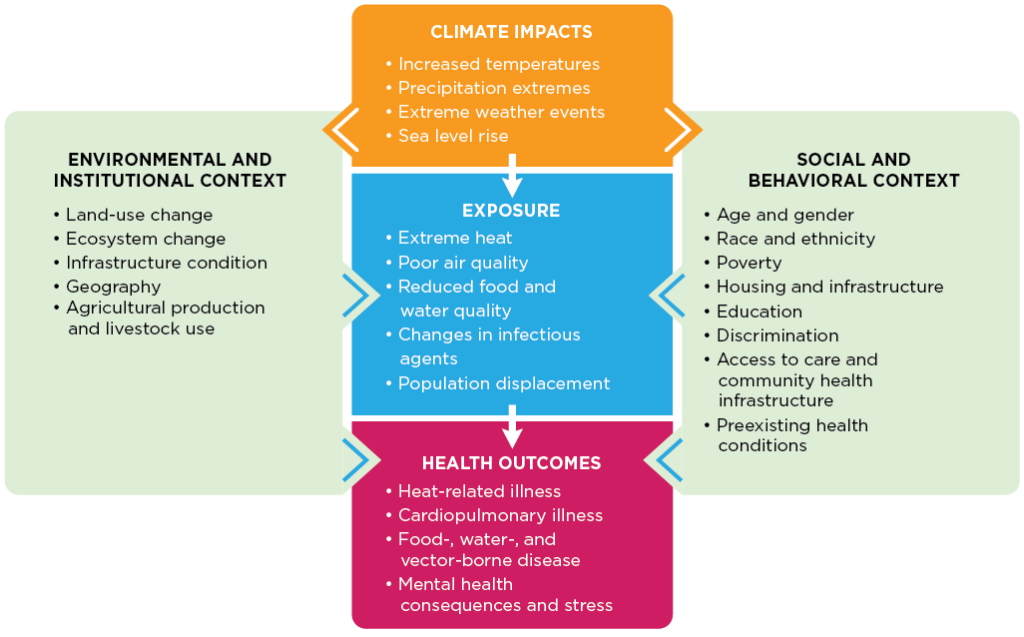
A report completed by The U.S. Global Change Research Program (USGCRP) created a simplified visual (figure 1) to showcase the different ways climate change adversely affects human health, which is often complex but tracking the changes and the root causes can help understand the health risk and create more push to develop solutions.
Another major cause of human health aligned with climate issues is electronic waste or e-waste. It is a significant contributor to human health problems. E-waste is generated by the disposal of electronic devices and products such as mobile phones, computers, and televisions. It is estimated that only 17.4% of total global e-waste is known to have been collected and properly recycled. These waste products contain toxic chemicals such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, which can harm human health when not disposed of correctly.
Improper disposal of e-waste can lead to these toxins leaching into the environment and contaminating soil, water, and air. This contamination can lead to a range of health problems, including respiratory and neurological damage, birth defects, and cancer. Furthermore, e-waste is often exported to developing countries, where workers are exposed to hazardous working conditions and are at risk of health problems.
So what can we do? Current assessments have implied that applying policies that involve the use of renewable energy, encouraging electric vehicles, preventing wasted food, smart management/operation of nuclear power, and more can result in the changes we need to see in order to save our health and the planet.
In conclusion, human health and the effects of electronic waste and climate change are deeply intertwined. E-waste is a significant contributor to health problems, and climate change poses a significant threat to human health. It is essential to take action to mitigate the impact of e-waste on human health and reduce the impact of climate change on our planet. By doing so, we can protect our health and well-being and ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.

As we build our insatiable demand for non-renewable sources, so does the mountain of minerals and metals that are becoming increasingly destructive to our environment. These are materials we use in different ways, from cell phones to radios; new technological innovations have in fact increased the use of electronic devices coupled with the resources diminishing slowly.
One of the central visions of Wastezon has centered around urban mining, a larger term for what we do here. Urban mining, coined in the 1980s by Professor Hideo Nanjyo of Tohoku University, is a concept that’s slowly gained traction worldwide. At the same time, we become more aware of its connection to electronic waste.
To be more specific, urban mining is the process of reclaiming raw materials from waste products sent to landfills. It looks toward the waste generated by cities and urban environments as a valuable resource, using man-made stocks rather than geological resources.
In the context of Electronic Waste, urban mining focuses on the process of recovering rare metals from discarded waste electrical and electronic equipment using mechanical and chemical treatments.
While actual numbers of the growing e-waste generated have been challenging to make certain of, efforts have been noted; according to a 2014 e-waste report released by the United Nations dictated that the majority of the 2014 global e-waste amounted to almost 60% and consisted of kitchen, bathroom and laundry equipment, while personal devices (phones, computer, etc.) was 7%, Other devices included screens, cameras, lamps and more.
All this tonne of electronic waste estimates to be roughly US$52 Billion in reusable resources, which is high in demand and toxic materials, yet low in availability. The Global E-Waste Monitor of 2014 gathered that this number of e-waste generated also resulted in “..some 16,500 kilotons of iron, 1,900 kilotons of copper, and 300 tonnes of gold..”. If mishandled, toxins like mercury leak into the earth and the air, affecting millions of people’s health.
With urban mining, for it to be successful without being detrimental to the environment things like product life cycle management must meet the needs for utilization of resources. This is where concepts like traceability work hand in hand with urban mining in order to have optimal recovery of the waste materials. By developing effective strategies and technologies, there is promise in being able to reduce the growing rate of e-waste and its dangers